Managing Risk at SICO

As the external risk environment becomes more and more complex, with heightened levels of both geopolitical and market volatility, the Risk Management function has become a critical component of SICO’s ability to remain a resilient organization that can meet its targets and create value for its stakeholders. SICO’s newly enhanced Risk Management function is responsible for identifying, measuring, and managing risk at both the group and business line levels. The department is continuously enhancing the framework that guides SICO’s day to day operations and decision-making in a manner that takes into account market conditions, complex new developments in technology, and the regulatory frameworks in each of the jurisdictions in which SICO operates.
While the GCC is faring relatively well in comparison to the rest of the world with expectations of comparatively healthy growth continuing in 2023, it is not immune to contagion, and it is vulnerable if global asset allocators begin a flight to safety and withdraw capital from the region. However, the recent success of two very high-profile events, the World Cup in Qatar, and the Dubai 2020 Expo, have brought renewed attention to the region. Later in 2023, the UAE is also set to host the COP28 climate summit which will further reinforce the GCC’s ability to successfully participate in global initiatives and set a strong example of global leadership.
SICO is a well-established financial institution with a diversified product offering and a footprint that currently includes three GCC markets, Bahrain, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE. We are ready and well positioned to meet the demands of these challenging times, delivering excellent returns for our clients. The Risk Management function at SICO is growing in strength and sophistication to deal with challenges, ensure that the highest fiduciary standards are met, and client expectations are exceeded.
External Risk Factors
In the time since the first outbreak and as the world has adapted to live with COVID-19 as an endemic pathogen, the post-pandemic world has become more complex and less cooperative.
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity has always been a constantly evolving challenge for modern financial systems, with commonly available AI tools now increasing the sophistication of phishing and other social engineering attacks. Today, cybersecurity poses one of the main threats to operational resilience to a wide range of industries, not only financial services. In fact, the overwhelming majority of CEOs and boards worldwide now classify cybersecurity as a business risk and not just a technology risk.
Geopolitics
Geopolitical risks are a key concern as the conflict between Russia and the Ukraine enters its second year. A close eye must be kept on primary and secondary effects of the conflict in Ukraine on supply chains and the price of agricultural and energy commodities.
Globalization
The era of globalization which has for decades governed the way business and “just-in-time” supply chains are managed and investments are made is rapidly deteriorating with souring relations among the major powers, conflict in Eastern Europe and escalating tensions between China and Taiwan.
The Security of Global Marine Transport
An increasing occurrence of threats to shipping in the Gulf region is indicative of a decline in the security of global marine transport which can result in critical choke points for energy and other commodities. The potential vulnerability of the system is evidenced by the attacks on oil tankers in the Gulf of Oman in 2019 and the drone attack on a gas transport ship in November 2022. High profile problems in the Suez Canal also highlight the potential risks to global supply chains if shipping networks are disrupted.
Inflation
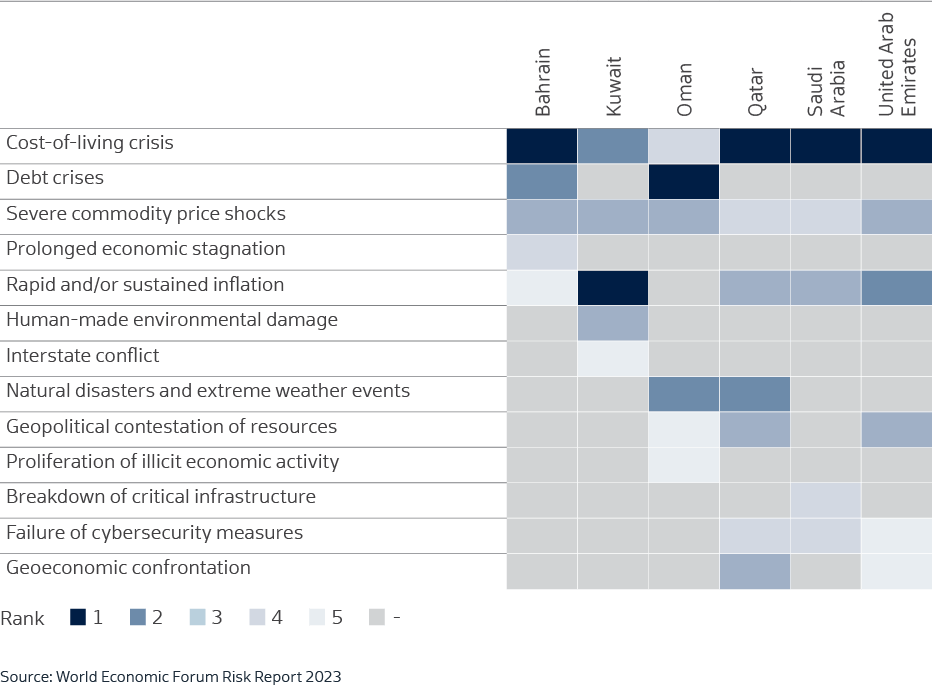
Inflationary pressures are being felt worldwide and the Gulf region has not been entirely spared. The “cost-of-living crisis” propagated by the impact of higher inflation and rising interest rates on economic growth in the region are impacting the market as major drivers of risk and features at the top of the list of concerns for regional executives surveyed by the World Economic Forum.
Higher Interest Rates
A global economic slowdown, rising inflation, slower growth, and higher interest rates will result in a concurrent tightening of margins and increased debt servicing costs for businesses. This will likely prove too great a burden for companies that are only able to survive in the era of cheap financing, flowing supply chains and lower costs. The rate of companies defaulting on their debt or being forced into restructuring or acquisitions will likely increase.
WEF GCC Risk Executive Survey Results 2023
Macro Hedging Strategies
The correlation of fixed income and equity markets during periods of heightened volatility will reduce the effectiveness of traditional macro hedging strategies. This change in the behaviour of asset class correlations is challenging longstanding concepts of portfolio management.
Climate Change
The escalating urgency of climate change and its impact on economies, and markets continues to dominate the global agenda as extreme weather events increase in frequency and severity, and conversations on loss and damage take center stage.
Demographics
Healthy demographics in the region, and the power to attract skilled labour from all over the world will continue to be beneficial for the GCC, even as other areas of the world face the demographic challenges of an aging workforce that places additional pressure on state services. Business and economic decisions taken now will have amplified effects on the future due to these demographic shifts. By increasing investment in training highly skilled GCC nationals, and focusing on economic diversification, GCC governments are planning and investing for the future.
Internal Risk Priorities
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity tops the list of SICO’s internal risks. Workshops organized for Bahrain’s banking sector by the Central Bank of Bahrain (CBB) have addressed the development of cybersecurity practices within the sector at large. SICO has also been represented at discussion forums on cybersecurity held by the Bahrain Association of Banks. In 2022 SICO further strengthened its cybersecurity practices by partnering with a leading cybersecurity services provider and bolstering its internal talent with the appointment of a new Information Security Officer with excellent credentials and expertise.
Credit Risk
SICO’s credit risk environment is stable with a high-quality set of controls in place to monitor fluctuations. We remain conscious of the macro economic challenges that can result in secondary impacts on credit risk, such as increasing default rates, and declines in the quality of collateral.
Changes in the Business
An ongoing rapid rate of change for SICO, presents a set of challenges, but the Risk Management function is an active partner to the business that is up to the task of ensuring that these developments and enhancements are delivered seamlessly without compromising the quality of the client experience or the resilience of operational processes. Our clients’ best interests are our top priority, and our fiduciary responsibilities are key.
Going Forward
The Risk Management function will assist SICO’s various business lines in identifying and managing potential sources of risk, ensuring that lessons learned, and industry best practices are applied across the organization. By identifying these risks, we can ensure that our business is resilient to potential external threats, and volatile market conditions and give further confidence to our clients and stakeholders.
Risk Management continually aims to be an effective partner to the front office and support functions, providing constructive and insightful challenge to current and proposed business practices and products, as necessary. By mapping out internal processes and controls we can rapidly identify new or changing risk factors and address any control vulnerabilities that may emerge in a resource efficient way.
An active and flexible Risk Management function at SICO ultimately gives the bank a competitive advantage to ensure that existing and prospective clients regard SICO as a top tier investment manager and leader in the risk management space; a “safe pair of hands” to be entrusted with their investments
